Leave Your Message
In the world of manufacturing, the choice of materials can significantly impact the quality and performance of the final product. One material that has gained considerable attention in recent years is technical ceramic. Renowned for its exceptional properties, technical ceramic offers a unique combination of strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it an ideal choice for various applications across multiple industries. The evolution of manufacturing technology and techniques has positioned technical ceramics as a viable alternative to traditional materials, such as metals and plastics, especially in environments that demand high performance and reliability.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the demand for materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity is on the rise. Technical ceramics exhibit remarkable resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal shock, making them perfect for harsh environments found in aerospace, medical, and automotive applications. In addition to their physical properties, these materials can also be designed to meet specific performance criteria, providing manufacturers with unparalleled versatility in their projects. By exploring the advantages of technical ceramic, manufacturers can make informed decisions that not only enhance product quality but also contribute to overall efficiency and sustainability in their production processes.
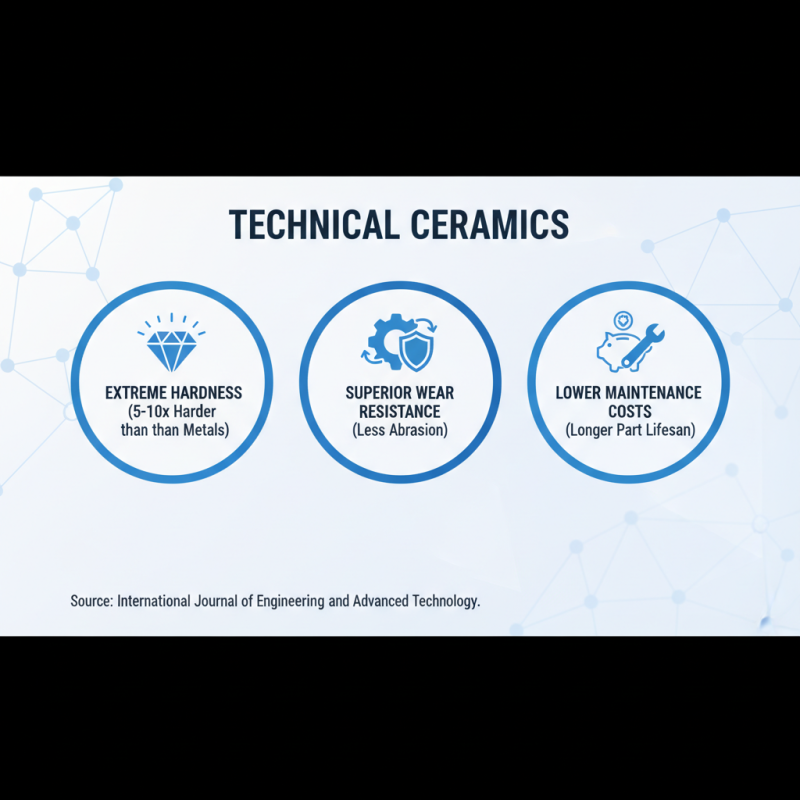
Technical ceramics have emerged as a pivotal material choice in various manufacturing applications, thanks to their unique properties. One significant advantage is their exceptional hardness and wear resistance. According to a report by the International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, technical ceramics can be five to ten times harder than metals, making them ideal for components subjected to high wear and abrasion. This hardness not only enhances the longevity of parts but also reduces the frequency of replacements, ultimately lowering maintenance costs in industrial setups.
Additionally, technical ceramics offer impressive thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures, making them suitable for usage in extreme environments. For example, the Global Ceramic Manufacturing Market report highlights that demand for high-temperature resistant ceramics is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15% through 2025. Such properties are invaluable in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where temperature fluctuations can compromise the integrity of traditional materials. By incorporating technical ceramics, manufacturers can achieve greater reliability and performance across their applications, contributing to more efficient production processes and enhanced product quality.
When considering materials for manufacturing projects, the differences between technical ceramics and traditional materials, such as metals and polymers, are significant. Technical ceramics are recognized for their outstanding properties, including high temperature resistance, hardness, and wear resistance. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the technical ceramics market is projected to reach approximately $24.6 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing application in industries such as aerospace and electronics, where the requirement for advanced materials continues to grow.
In contrast, traditional materials, while widely used, often do not match the performance characteristics of technical ceramics under extreme conditions. Metals, for example, can deform and lose strength when subjected to high temperatures, whereas ceramics maintain structural integrity even at elevated temperatures. Furthermore, ceramics exhibit superior chemical resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments. A study published in the Journal of Materials Science highlighted that technical ceramics can withstand corrosive substances better than conventional materials, leading to increased longevity and reduced maintenance costs in application scenarios.
The evolution towards advanced manufacturing technologies, including additive manufacturing, is further emphasizing the advantages of technical ceramics. The incorporation of these materials not only enhances product performance but also enables designers to explore innovative solutions that were previously unattainable with traditional materials. As industries strive for efficiency and sustainability, the shift towards technical ceramics is becoming increasingly pronounced, promising to reshape the landscape of manufacturing.
| Property | Technical Ceramics | Traditional Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (7-9 Mohs) | Moderate (2-5 Mohs) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent (up to 2000°C) | Limited (up to 600°C) |
| Electrical Insulation | Very Good | Variable |
| Wear Resistance | Superior | Lower |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Generally lower |
| Weight | Lightweight | Varies (often heavier) |
Technical ceramics are increasingly being recognized for their exceptional properties that make them an ideal choice for various manufacturing applications. One of the most notable characteristics of technical ceramics is their high hardness and wear resistance. This makes them suitable for use in environments where abrasive materials are present, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance costs. Additionally, their mechanical strength under high temperatures allows them to maintain structural integrity, making them invaluable in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Another key property of technical ceramics is their excellent thermal stability and insulating capabilities. Unlike metals, ceramics can withstand extreme temperatures without deforming or losing their functional properties. This thermal resistance not only enhances durability but also contributes to energy efficiency in manufacturing processes. Furthermore, technical ceramics are chemically inert and non-reactive, which minimizes the risk of contamination in sensitive applications, such as in the production of semiconductors or medical devices. These features collectively position technical ceramics as a reliable option for engineers seeking materials that offer both performance and cost-effectiveness in their manufacturing projects.
Technical ceramics are increasingly becoming the material of choice across various industries due to their unique properties and versatility. In the aerospace sector, for instance, technical ceramics are utilized to enhance the performance of engine components and thermal protection systems. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh environments makes them ideal for critical applications, reducing the risk of failure and improving the efficiency of aircraft.
Furthermore, the medical industry has also recognized the advantages of technical ceramics. These materials are employed in the manufacturing of implants and dental applications due to their biocompatibility and resistance to wear. The inert nature of ceramics ensures that they can safely coexist with body tissues, making them an excellent choice for devices intended for long-term use. The precision and durability of technical ceramics contribute significantly to the longevity and reliability of medical devices, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.
In the electronics sector, technical ceramics provide essential benefits for insulating and substrate applications. Their electrical insulating properties are crucial for manufacturing components such as capacitors and insulators that operate under high voltages. Additionally, the thermal conductivity of certain technical ceramics enables efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices, ensuring optimal performance and safety. As industries continue to innovate, the demand for technical ceramics is expected to grow, driven by their superior characteristics and the broad range of applications they support.
When considering technical ceramics for manufacturing projects, it's essential to address the inherent challenges that may arise during their application. One of the predominant challenges is the brittleness of ceramic materials compared to metals or polymers. This fragility can lead to issues during the machining process, as well as during the handling and assembly of components. To mitigate these risks, manufacturers often employ advanced machining techniques and careful handling procedures, ensuring that the ceramics are supported adequately throughout their processing and integration stages.
Another challenge lies in the limited understanding of the thermal and electrical properties of technical ceramics among engineers and designers. Misinterpretations of these properties can lead to suboptimal material selection for specific applications. To combat this, ongoing education and training are crucial for professionals in the field. Implementing simulation tools and material testing can also aid in maximizing the performance of technical ceramics in real-world scenarios, allowing for better alignment with project requirements and ultimately leading to more successful manufacturing outcomes.